Evacuations from High-Risk Locations Call +44 (0)1202 308810 or Contact Us →
Election violence in Kenya

Situation Summary of Election Violence in Kenya
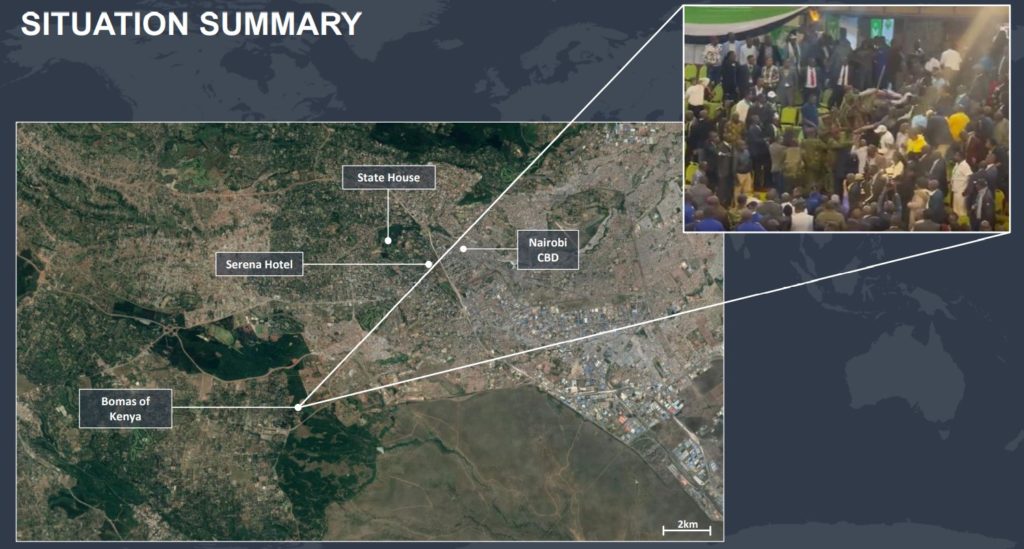
On 15 August, violence erupted at the Bomas of Kenya in Nairobi, as the Independent Electoral and Boundaries Commission (IEBC) had been scheduled to release the results of the Kenyan general election. Live footage from the venue showed physical altercations breaking out between attendees, with military
personnel intervening to break up the violence.
Earlier on 15 August the IEBC had announced a delay in releasing the results, although did not specify a reason for the delay. Separately, four commissioners of the IEBC held a press conference at the Serena Hotel in Nairobi, in which they stated that they could not “take ownership of the results” due to concerns over their opaqueness. As the violent scenes emerged and news broke of the division within the IEBC, it
was announced that riot police across the country had been placed on standby, with Kenya’s highest bishop calling for calm and peace to prevail.
In the days since the 9 August election, the IEBC has been verifying the vote tallies provided by the country’s polling stations. In this interim period, both main presidential candidates have alluded to voting irregularities and of fighting the result in courts. Meanwhile, the delay between voting and the announcement of a result had only led to further speculation and disinformation around the legitimacy
of the vote.
Around 20 minutes after the initial chaotic scenes at the Bomas of Kenya, and despite four of the seven IEBC commissioners stating they could not back the results, the IEBC announced that William Ruto had won the election with 7,176,141 votes – amounting to 50.49 percent of the total valid votes. The pre-election favourite, Raila Odinga, received 6,942,930 votes – representing 48.85 percent of the votes cast.
Solace Global Comment
In 2007, post election violence resulted in more than 1,500 civilian deaths, whilst in 2017 at least fifty were killed and the election result was seen as so contentious that the country’s Supreme court ruled the vote should be re-run. Odinga has run for president on five occasions and has lost each time he has run.
He has also disputed the final election result following each loss, which set the conditions of suspicion and mistrust, and ultimately precipitated previous outbreaks of post-election violence. Given that Odinga was seen as the favourite to win the Presidency during the 2022 election, the closeness of the declared result and the inconsistency from the IEBC on 15 August, it is highly likely that he will once more
attempt to contest the election results.
Regardless of whether Odinga officially disputes the result, it is highly likely that his supporters will rally against the result. Any such unrest is highly likely to become violent. The city of Kisumu, which is home to a large pro-Odinga voting bloc, has already begun to see protests break out against alleged vote rigging, whilst in the Kibera area of Nairobi there are reports that riots have begun to break out. Further
unrest is likely to remain centred on the political centres of gravity in Nairobi, with the State House, Central Business District, and Serena Hotel all probable areas of unrest in the short term.
It is noteworthy that this was the first election in which there was no candidate from Kenya’s largest tribe, the Kikuyu. As a result, if election violence and unrest begins to spread across the country, there is a realistic possibility that it will avoid the traditional split along ethnic and tribal lines. Consequently, post-election violence may occur more widely across Kenya, as it would not be centred on tribal population centres, although it may be less extreme than levels observed during previous elections in which a Kikuyu candidate was participating.
Solace Global Advice
• Widespread unrest and violence remains possible in the short term. Travellers should avoid all demonstrations and large public gatherings as they may escalate quickly and without warning. Immediately vacate the area if caught in unrest.
• In the event of a significant security development, travellers in Kenya should follow any instructions issued by the Kenyan government or local authorities.
• Areas where political figures are known to gather are likely to be focal points for political activism and unrest, especially sites associated with the Presidential office or known protest hotspots. You should be particularly vigilant in these areas and follow any specific advice from the local security authorities.
• Expect localised travel disruption and an enhanced security force posture in the short-term. Allow for additional time when travelling in-country, as protest action and increased security force presence may result in road closures or blockades.
• Ensure that you always carry personal identification documents. Consider making photocopies of important documents in case of confiscation, theft or loss.
• Make sure you are familiar with contact details for the emergency services in Kenya – dial 999 / 112 / 911 to request police, medical assistance or fire brigade.
• Exercise increased caution, remain vigilant, be aware of your surroundings and report any suspicious activity to security personnel as soon as possible.
• If caught in the vicinity of a security incident, seek shelter immediately and leave the area if safe to do so. Continue to adhere to all instructions issued by authorities and obey any security cordons in place.
• Report any suspicious items and behaviours to the nearest security or police officials.
• Monitor the Solace Secure platform and local media for updates.
Support for operations in Kenya
Our team of risk management specialists and intelligence analysts, combined with on-the-ground security support from our global partner network can help secure your operations.
Learn more about how we can secure your operations